AEM deployment options
1. Introduction to AEM deployment options
-
In Adobe Experience Manager (AEM), one of the first decisions you’ll face is how to deploy it. AEM offers three main deployment types: on-premise, Adobe Managed Services (AMS), and AEM as a Cloud Service (AEMaaCS). Each option has its unique strengths and challenges, making it essential to pick the one that aligns with your project’s needs.
-
On-premise gives you complete control over your infrastructure, AMS offers Adobe’s expertise in managing hosting, and AEMaaCS provides a modern, scalable cloud-native solution. Understanding these options is the first step toward setting up a reliable and efficient AEM environment.
-
Let’s see the three main deployment types
-
- AEM on premises
- AMS – Adobe Managed Service (mainly hosted on AWS)
- AEM as a Cloud Service (AEMaaCS)
2. AEM On-Premises Architecture
- AEM on-premises architecture is a traditional deployment model where the AEM instances are hosted within an organization’s own data center or on their private cloud. This model gives organizations or companies complete control over their infrastructure, security, and compliance.
Key benefits
- Control: Complete control over the infrastructure, security, and compliance.
- Customization: High flexibility for customization and integration with existing systems.
- Security: Direct control over security policies and data protection measures.
Challenges
- Cost: Higher upfront and ongoing costs for hardware, maintenance, and staffing.
- Complexity: Requires skilled IT staff to manage and maintain the infrastructure.
- Scalability: Scaling resources can be more complex and slower compared to cloud solutions.
3. Key Components of AEM On-Premises Architecture
- Author Instance
- Publish Instance
- Dispatcher
- Database
- File System
- Replication Agents
- Backup and Recovery
4. Detailed Explanation of Components
-
Author Instance
-
- The Author instance is where content creators, editors, and marketers work. It is used for creating, editing, and managing the content
- Features
- Content creation and editing
- Workflow and approvals
- Versioning and content management
- User and group management
- Integrated tools for digital asset management.
-
Publish Instance
- The Publish instance is responsible for delivering the content to end users. It serves the content through websites, mobile apps, and other channels.
- Features
- High-performance content delivery
- Scalability to handle large volumes of traffic
- Secure delivery of published content
- Integration with CDNs for global reach
-
Dispatcher
- Dispatcher is a caching and load-balancing tool used to increase the performance of AEM. It caches content to reduce the load on the publish instances and balances the load among multiple publish instances.
- Features
- Caching of HTML, images, and other static content
- Load balancing across multiple publish instances
- URL filtering and security enhancements
-
Database
- The database is used to store content metadata, user data, and configuration settings. AEM supports various database systems such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, and others.
- Features
- Storing content metadata and configuration
- Ensuring data integrity and consistency
- Supporting transactional operations and queries
-
File System
- The file system is used to store binary content such as images, videos, and other digital assets. These files are usually stored in a shared storage system accessible by AEM instances.
- Features
- High-performance storage for large files
- Support for distributed and shared file systems
- Integration with AEM for asset management
-
Replication Agents
- Replication agents are responsible for transferring content from the author instance to the publish instances. They ensure that the latest content is available for end users.
- Features
- Reliable and secure content transfer
- Support for scheduled and on-demand replication
- Monitoring and logging of replication activities
-
Backup and Recovery
- Ensures that content, configurations, and system states can be restored in case of data loss, corruption, or system failures.
- Features
- Regular backups of databases and file systems
- Automated backup schedules and policies
- Disaster recovery planning and implementation
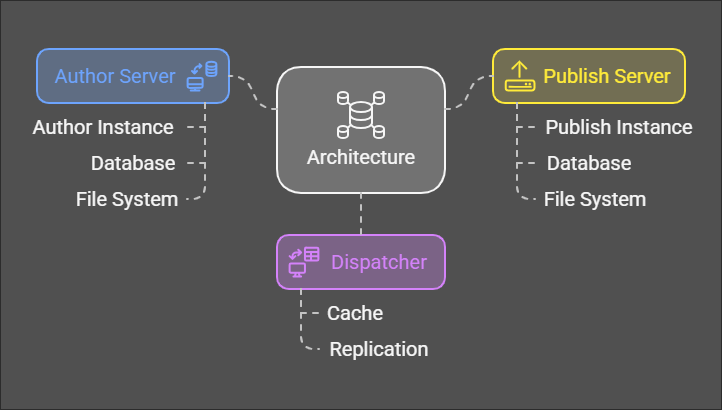
AEM on-premises architecture is suitable for organizations with stringent compliance, control, and customization requirements, providing full control over the entire content management infrastructure.
5. Adobe Managed Services (AMS) Architecture
-
What is AMS?
- AMS provides AEM as a managed service hosted on Adobe’s cloud infrastructure. Adobe takes care of hosting, updates, and maintenance, while you focus on creating and delivering content. More details
-
Benefits of AMS (expert support, reduced infrastructure management).
-
Reduced infrastructure management overhead.
-
Expert support from Adobe for hosting and operations.
-
Predictable costs with managed scaling.
-
-
Use cases where AMS is a good fit.
- AMS is ideal for organizations that need reliable hosting without the complexity of maintaining on-premise infrastructure but still want some control over their AEM instances
6. Comparison between On-Premise, Managed
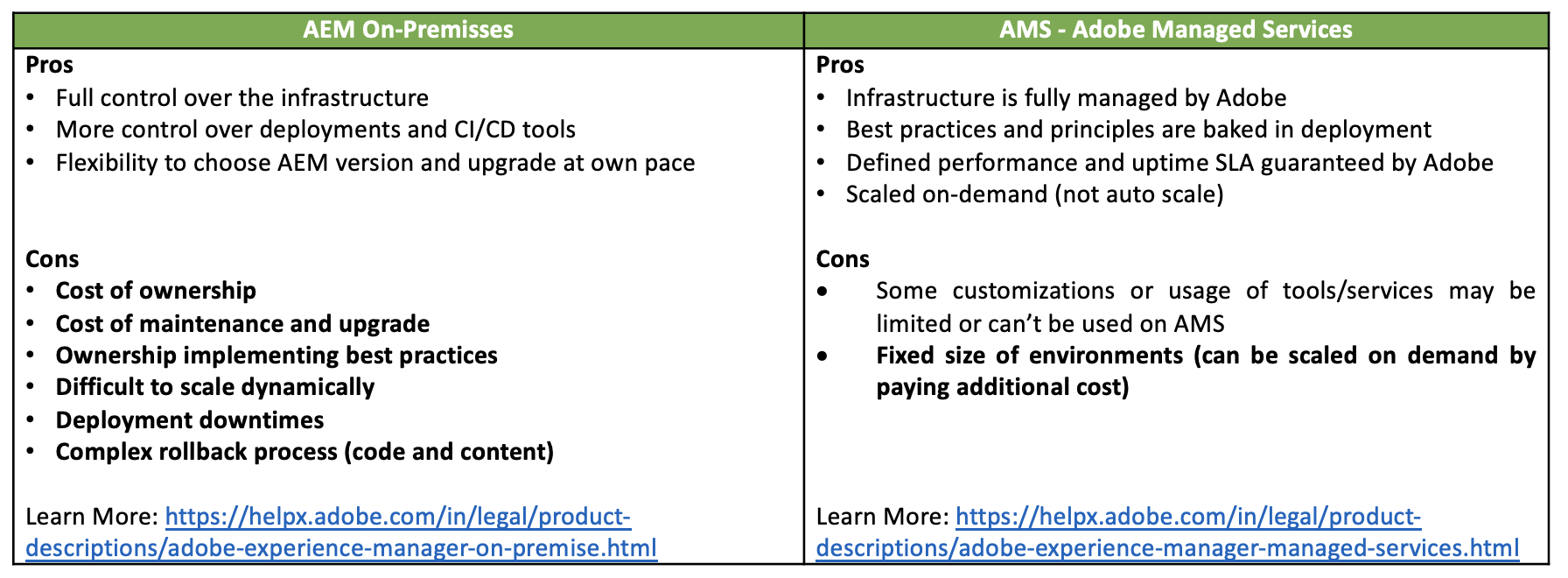
-
Also, some challenges exist in both offerings (above):
- Scalability limitation because of the way the Oka/JCR repository works in classic AEM
- Computational limitations (e.g., asset processing and rendition generation)
- Content replication-related issues (performance, reliability, etc.)
-
Some of these limitations (highlighted) directly translate into a need for a cloud-native solution so that AEM can be scaled, and inherit the security benefits of the cloud along with a lower cost of ownership, therefore, Adobe came up with AEMaaCS offering.
-
For now, consider that the old classic AEM has been refactored into the following:
- A containerized architecture for scalability and to make AEM cloud-native
- Set of smaller and scalable services (repository service, asset computer service, etc.) for extensibility and performance improvements
7. What is AEM as a Cloud Service?
AEM as a Cloud Service (AEMaaCS) is the cloud-native version of Adobe Experience Manager, designed to leverage the benefits of cloud computing to deliver more agility, scalability, and resilience. It is part of the Adobe Experience Cloud and offers a range of features optimized for cloud deployment. more details
-
AEM as a Cloud Service let us explore the feature
-
Scale your DevOps efforts with Cloud Manager: CI/CD framework, autoscaling, API connectivity, flexible deployment modes, code quality gates, service delivery transparency, and guided updates.
-
Enable developers to add automation to application development practices.
-
Deliver content quickly and efficiently on a global scale, using a built-in Content Delivery Network (CDN) and other network-layer best practices.
-
Leverage a dynamic architecture that auto-scales, thus removing infrastructure considerations.
-
Stay on top of threats and security risk mitigation, using automated tests to scan for common vulnerabilities.
-
Ensure maximum resilience and efficiency backed by optimized performance topologies.
-
Take advantage of AEM as a Cloud Service’s deep integration with the Adobe Experience Cloud to provide better customer experiences with online marketing and web analytics products.
-
Utilize tools that help accelerate the migration tasks, such as code refactoring, transfer of content, and more.
-
8. Typical AEM as a Cloud Service environment
-
A new project that is getting onboarded on AEMaaCS will be provisioned under a Program. There are three types of environments available with a Program of AEM as a Cloud Service:
- Production environment: hosts the applications for business practitioners.
- Stage environment: is always coupled to a single production environment in a 1:1 relationship. The stage environment is used for various performance and quality tests before changes to the application are pushed to the production environment.
- Development environment: allows developers to implement AEM applications under the same runtime conditions as the stage and production environments.
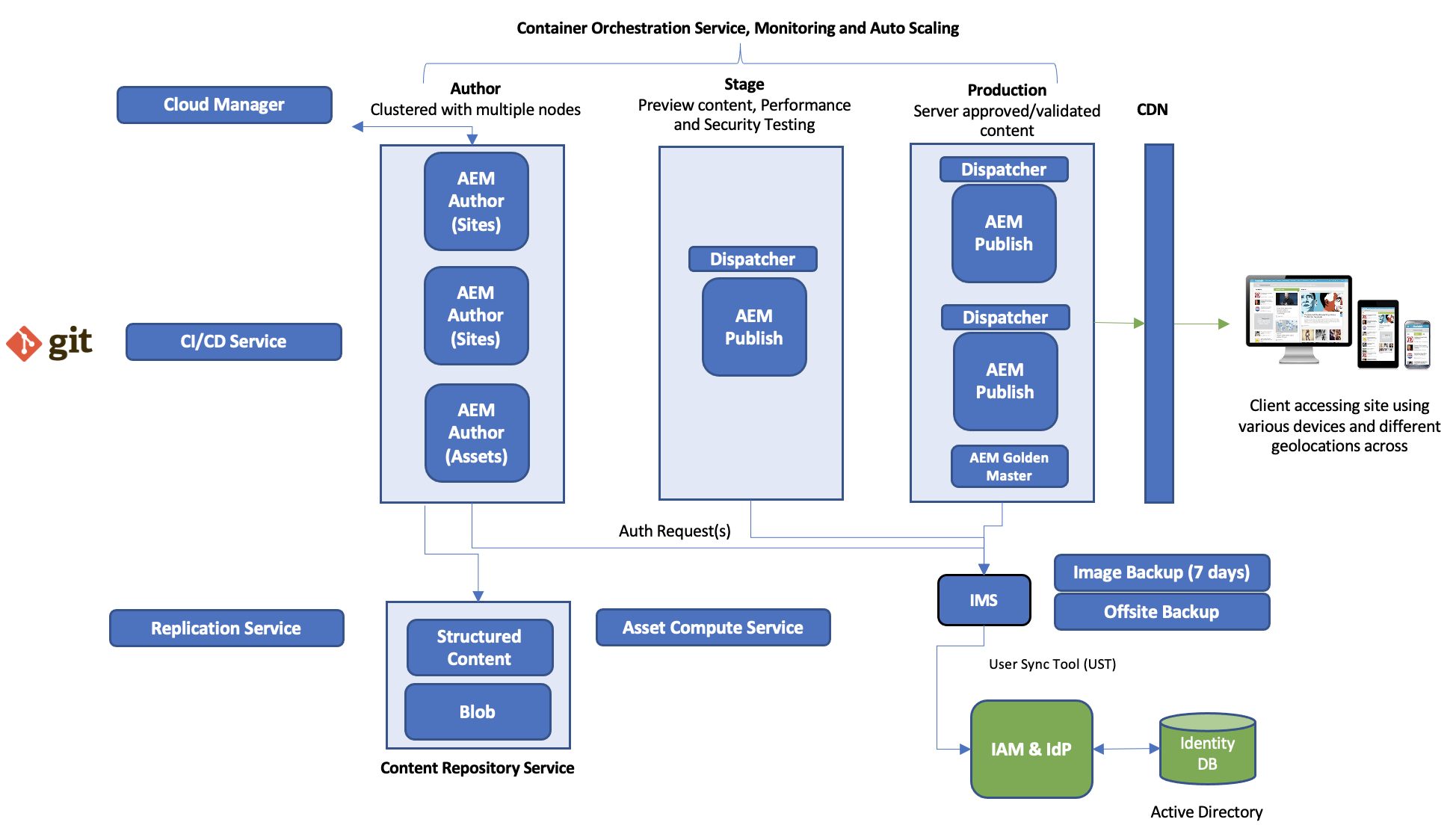
-
Any new AEM project is always bound to exactly one specific codebase, where you can store both configuration and custom code for your project. This information is stored in a code repository, accessible via the usual Git clients, and made available to you at the time new programs are created.
- AEM Cloud Sites Service
- AEM Cloud Assets Service
Both of these allow access to several features and functionalities. The author tier will contain all Sites and Assets functionality for all programs, but the Assets programs will not have a publish tier, nor a preview tier, by default.
9. Core benefits of AEM as a Cloud Service:
- It is always on with zero downtime
- It is always at scale
- It is always current with the latest features/upgrades
- It is always evolving (Adobe is adding new sets of standards and best practices, those are by default included automatically)
- Low cost of ownership
- Usage-based license model
- More secure as it is always on the latest security level
10. Why AEM as a Cloud Service?
why AEM as a Cloud Service, we need to look at the expectations of consumers and businesses in today’s era. Also, we need to look at the limitations/challenges with either AEM classic/on-premises or AMS.
-
At high-high customers want:
- Better experience (personalization, just-in-time experience)
- Relevant content/information
- Fast and seamless experience
-
On the other hand, businesses expectation is:
- Customer satisfaction
- Lower cost of delivery
- Self-resilient applications/IT infrastructure
- Modernized and scalable applications
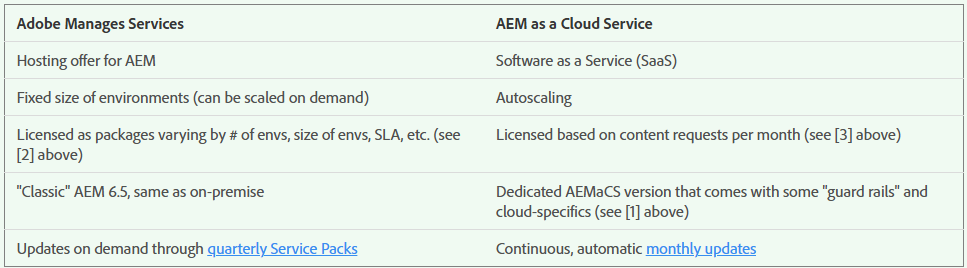
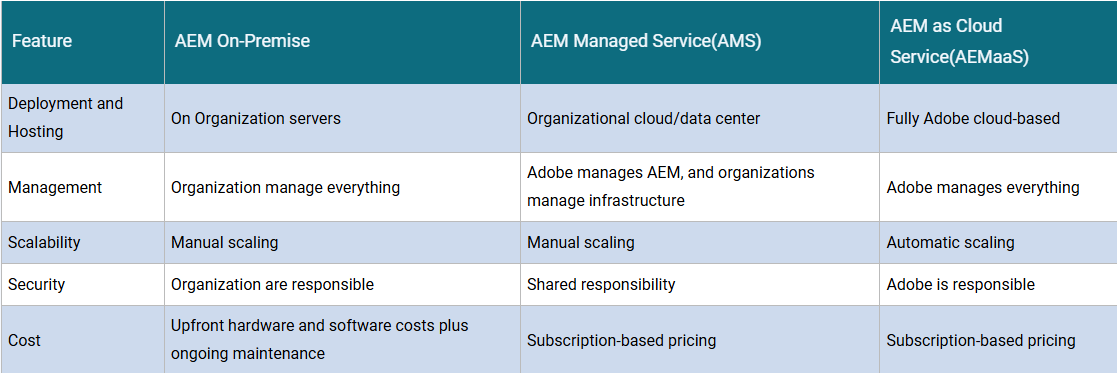
11. Comparison between On-Premise, Managed & Cloud deployment
12. Important Links for more information
https://helpx.adobe.com/legal/product-descriptions/adobe-experience-manager-managed-services.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/legal/product-descriptions/aem-cloud-service.html
Every great discussion starts with a simple thought! If you enjoyed this article, found it useful, or have any questions, let’s talk! I’d love to hear from you.
For more updates, tips, and engaging conversations, connect with me on Medium, LinkedIn, and RealCodeWorks. Let’s keep learning together! 🚀✨
Thank you 🙏 !