AEM Instances and Environments
1. AEM Instances Overview
AEM operates through different instances, each playing a specific role. Let’s break them down:
- Author Instance
This is your workspace. It’s where content authors create, edit, and manage the content. Think of it as the “back office” where all the magic happens before content goes live. - Publish Instance
Once your content is ready to go public, it gets pushed to the publish instance. This is the “front stage” where your audience interacts with the live content on your website. - Dispatcher
Picture this as the gatekeeper. The dispatcher handles caching and load balancing. It speeds up content delivery by storing frequently accessed pages and spreads the load across servers so none of them gets overwhelmed. - Other Instances
Depending on your setup, you might have extras like preview instances (to check how things look before going live) or replication agents (to move content between instances). Each one has a unique role in keeping things running smoothly.
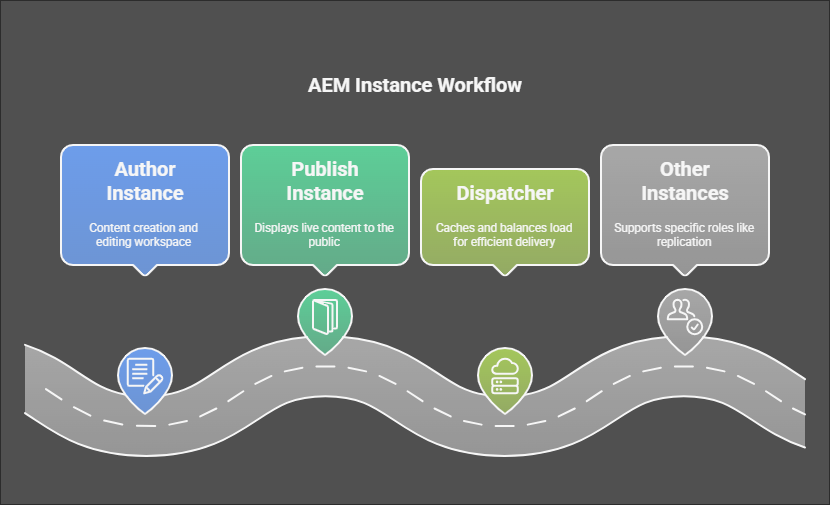
Together, these instances make sure content flows seamlessly from creation to publication.
2. Understand AEM Environments
Now let’s talk about environments. These are the stages your content and code pass through before going live:
-
Development Environment: This is where developers begin. It’s a space for coding, and testing new features. Developers can experiment and troubleshoot here without affecting anything live.
-
QA Environment: After development, the code moves into the Quality Assurance (QA) environment. This is where the QA team checks for bugs, and issues, and ensures everything works properly before it gets approved for the next step.
-
UAT Environment: Once the code passes QA, it enters the User Acceptance Testing (UAT) environment. Here, users or stakeholders check if the new features meet the business requirements and overall expectations. It’s a final check before going live.
-
Staging Environment: After passing UAT, the code is deployed to staging. This environment mirrors the production environment, giving a final chance to test everything together and make sure nothing breaks before it reaches the live site.
-
Production Environment: Once everything is checked and approved, the code reaches the production environment. This is where the site is live, and it handles real-time user traffic. It’s optimized to ensure the best possible experience for users
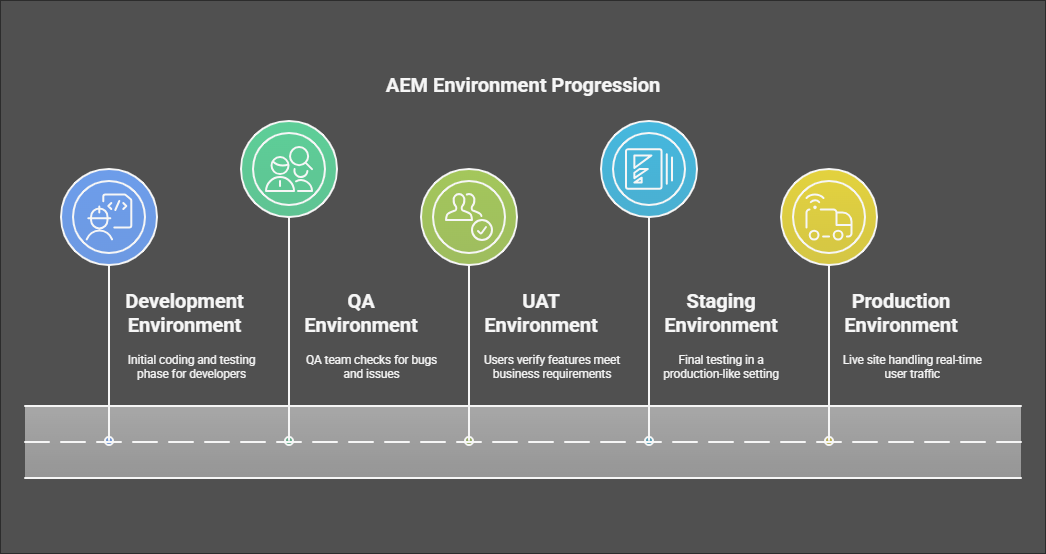
Each environment has a specific purpose, ensuring the content and code are polished before reaching users
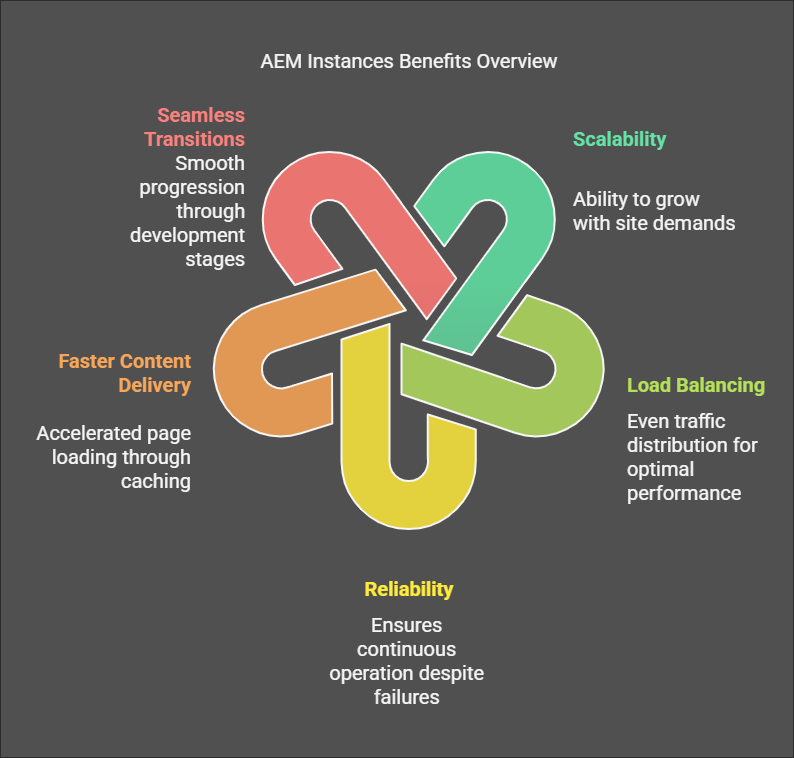
3. Why Instances Matter for Smooth Content Delivery
Here’s how AEM instances help keep your site running smoothly
-
Scalability: As your traffic grows, you can add more instances to handle the load. This ensures your site stays fast and responsive, no matter how much it scales.
-
Load Balancing: Load balancers distribute user traffic across multiple instances. This keeps any single server from getting overwhelmed, even during peak times.
-
Reliability: With multiple instances, your site won’t go down if one fails. Another instance can take over, ensuring uninterrupted access for your users.
-
Faster Content Delivery: AEM’s caching system speeds up content delivery. Pages load faster for repeat visitors, improving the overall user experience.
-
Seamless Transitions: From development to production, each environment ensures smooth handoffs. Bugs are fixed in QA, staging tests everything, and production delivers a polished experience to users.
Conclusion
For more updates, tips, and engaging conversations, connect with me on Medium, LinkedIn, and RealCodeWorks. Let’s keep learning together! 🚀✨
Thank you 🙏 !